
Food Safety Focus (218th Issue, September 2024) – Article 1
Practical Tips for Food Storage with Refrigerators and Freezers
Reported by Mr. Kenneth YIP, Scientific Officer,
Risk Communication Section, Centre for Food Safety
Refrigerators and freezers are indispensable equipment for food storage. Proper food storage is essential to ensuring food safety as well as quality. This article will discuss the pros and cons of refrigeration and freezing, explain what kinds of food should be stored in the fridge and their storage periods, and the proper practices to keep food safe in the fridge.
Refrigeration versus Freezing – Are They the Same?
While both refrigeration and freezing can preserve food by keeping it cold and out of the Temperature Danger Zone, the conditions under which food is preserved are not identical. Refrigerated foods are kept at 4°C or below, when the growth of many types of bacteria will be inhibited. Most foods can maintain their textures upon storage under refrigeration. However, some types of bacteria like Listeria monocytogenes can still thrive at refrigerated temperatures. It is worth noting that if present, it can proliferate in the refrigerator over time and lead to foodborne illness.
In contrast, bacteria are forced to enter a dormant stage when foods are stored at -18°C or below. When compared with refrigeration, food spoilage is minimised because microbiological development is inhibited. Besides, freezing food like fish at –20°C or below for seven days or at –35°C for about 20 hours can kill parasites in food manufacturing processes. However, some foods may face food quality issues upon freezing, which include freezer burn in frozen meats, fat bloom (whitish or greyish coating) on chocolates and unstable oil-in-water emulsions (discrete aqueous and oil layers) in mayonnaise, making them unsuitable for food preparation. Prior to freezing or refrigerating food, it is advisable to prepare ahead and inspect which items can be kept fresh and nutritious.
Food Types and Storage Periods in the Fridge
Refrigeration and freezing are widely adopted in storing perishable foods including meats, seafoods and processed foods like sausages. Nevertheless, not all food items are suitable to be kept in the fridge. Fruit and vegetable crops like banana may be susceptible to chilling injury (damage or deterioration which occurs when food is exposed to temperatures below their optimal storage temperature). Chilling injury is a physiological response that can shorten shelf life in addition to reducing product quality. In Besides, shell eggs should not be put into freezers. Freezing shell eggs may alter their egg protein structure and may cause the shells to crack. Eggs should be stored in the refrigerator rather than frozen.
While some may think that refrigerated and frozen foods have significantly longer shelf lives, it is important to remember that keeping times vary depending on the types of food. Refrigerated foods can still be spoiled after prolonged storage. Foods like fresh poultry could be kept for days for safe consumption. Of note, once the packaging of prepackaged food is opened, the date mark may become irrelevant. Follow the manufacturer's instructions for storage time and conditions after opening.
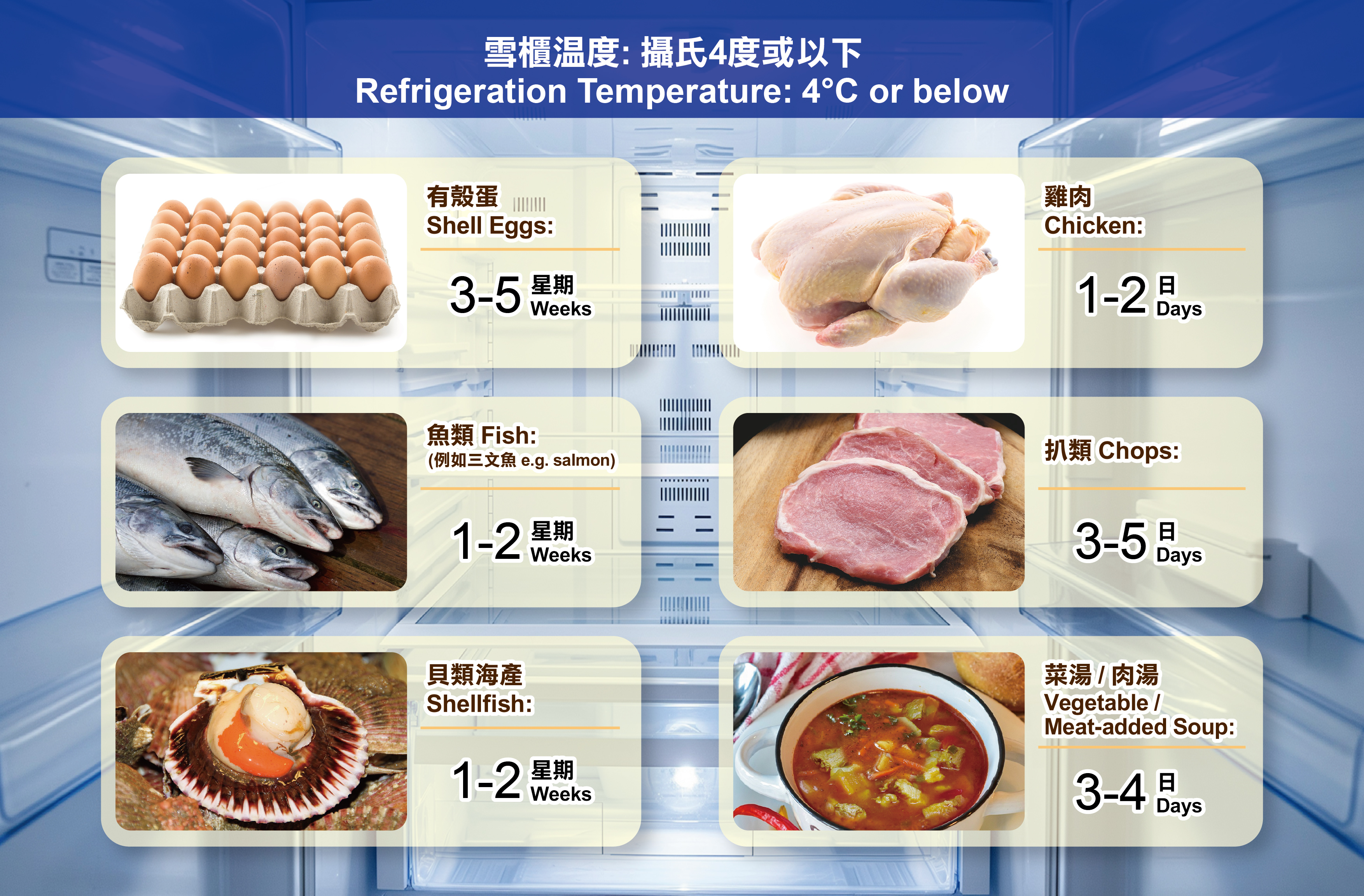
Figure: Storage period of some refrigerated food
(Source: Food and Drug Administration https://www.fda.gov/media/74435/download)
Keys for Keeping Foods Safe – Proper Separation and Sanitation
Separating raw foods from ready-to-eat (RTE) and cooked foods is essential to avoiding cross-contamination. Foods should be stored in covered or sealed containers before they are put into the fridge or freezer. Raw foods should be stored below RTE or cooked foods to prevent their juices from dripping onto other foods and hence causing cross-contamination. For large scale food storage, it is preferable to have different cold storage equipment for separating raw foods from RTE and cooked foods. Besides, fridges should be cleaned regularly.
Key Points to Note
- Refrigeration and freezing preserve foods by keeping them cold but under different conditions.
- While refrigeration and freezing can be used to store a wide range of foods and extend their shelf lives, these methods may not be suitable for preserving some food items.
- When refrigerating or freezing foods, raw foods should be separated from RTE and cooked foods.
- Clean the fridge compartments regularly.
Advice to the Public
- Keep appliance thermometers for refrigerators and freezers without temperature monitoring devices and check the readings regularly.
- Follow the 2-hour / 4-hour rule for storing RTE and cooked foods into the fridge.
- Always keep fridge doors closed.
Advice to the Trade
- Check the temperature log graphs of cold storage devices to make sure they function properly.
- Allow sufficient capacity for bulk storage of food stock.
- Maintain and service refrigerators regularly.







